Documents unearthed a week ago show Environment Minister Edna Molewa signed the approval for mining in the Mabola protected environment on August 20 2016, three months before Minister of Mineral Resources Mosebenzi Zwane signed it on November 21.
The permission for Indian company Atha Africa Ventures to mine in Mabola, a critical water catchment area near Wakkerstroom, became effective on the date Zwane signed — although neither department publicised the decision.
The ministers sent a letter to Atha Africa, but it did not become public until the Centre for Environmental Rights (CER) unearthed it among other documents the centre had requested from the government.
Explaining their decision in the letter, the ministers cited the fact that Atha Africa had obtained the legally required licences and permits necessary for a mine. The decision appears to set the same bench marks for mining in a protected environment as anywhere else, and critics are concerned about the precedent this sets.
“What we now have is apparently a situation where those two ministers can simply talk to each other, have no public consultation, not tell anyone about the request they’ve received, and then just allow mining to go ahead in any of our protected areas,” said CER executive director Melissa Fourie.
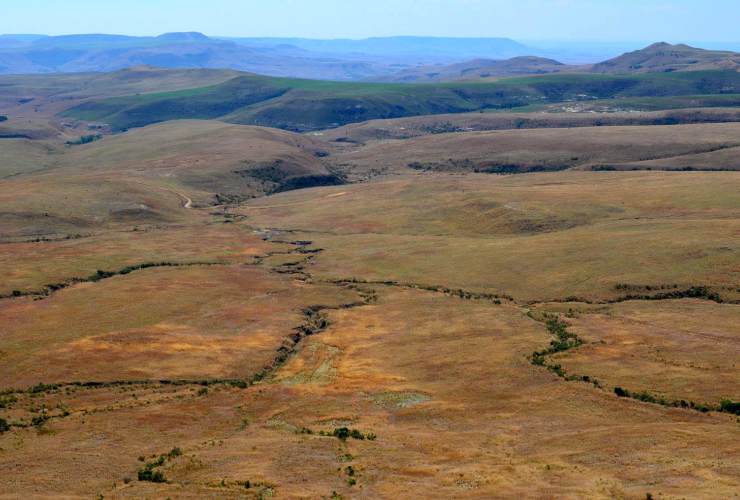
Mabola falls within a strategic water source area that feeds the catchments of the Vaal, Pongola and Tugela rivers
Protected areas
While the company held public participation meetings with affected landowners in early 2015 — a prerequisite for gaining mining-associated permits — neither the department of environmental affairs nor the department of mineral resources involved the public in the decision to grant approval to the mine.
The Protected Areas Act is ambiguous in terms of public notice, and affected parties continue to debate the necessity of such engagement.
After Oxpeckers reported in February 2015 that Atha-Africa planned to mine coal in the critical water catchment area, the proposal has faced court action from a coalition of civil society organisations led by the CER. Because Mabola is demarcated as a protected environment, mining could only proceed if approved by the ministers of both departments.
In October 2016 Oxpeckers reported that the mine had been granted a water use licence and environmental authorisation by the Mpumalanga provincial authorities – and that the only regulatory roadblock remaining was the go-ahead from the environment minister.
The approval letter that Molewa had already signed by then (see document below) cites the mine’s compatibility with the draft Mabola protected environment management plan and the Mining and Biodiversity Guidelines as reasons for giving it the go-ahead.
Operations timeline
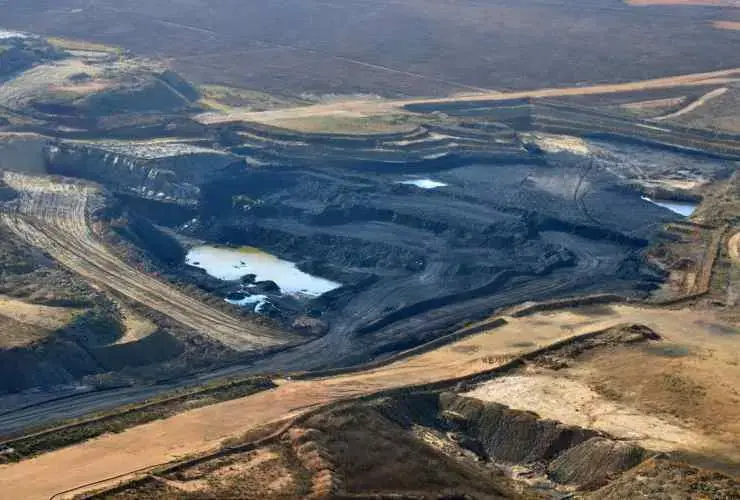
Atha-Africa holds an 8,360ha mining right over 12 farms, and plans to use 2,500ha of the right. Known as the Yzermyn underground coal mine, the operation would tunnel under veld currently used for grazing and could operate for 15 years.
According to Atha-Africa representatives, the company does not plan to expand the size of the mining area for at least a decade, if it does at all.
BHP Billiton held the prospecting right before transferring it to an outfit called Bunengi Mining in 2011. Atha Africa then bought the right from Bunengi.
Representatives from Bunengi were not available to comment on why they sold the right to Atha-Africa, part of one of the oldest mining companies in India, the Atha Group.
A representative from BHP Billiton said the reason behind its sale of the right would be difficult to track down, but it was likely to be part of the company’s broader downsizing in South Africa that included the spin-off of South32 in 2015.
In a statement sent to Oxpeckers, Atha Africa laid out its timeline for beginning operations: “Atha Africa Ventures intends to issue build contracts by May 2017 and construction is due to begin from the middle of June 2017.”
Covering 8,772ha, the Mabola catchment is identified as critical for both provincial and national biodiversity initiatives. It falls within a strategic water source area that feeds the catchments of the Vaal, Pongola and Tugela rivers.
“Atha Africa is confident that its mitigation plans will ensure that, by the time the life of mine ends, the wetland is at the same baseline condition, if not better,” the company said.
Yzermyn’s footprint on ground level will be contained to 22.4ha, about half of which will directly impact the wetlands, Atha-Africa said. The mine’s water use licence allows the use of 56,554 cubic metres of water a year, as well as the disposal of some treated effluent in wetlands.
The approval to mine in a protected environment came with minimal caveats aside from the stipulations in the water use licence, mining right and other documents that every mine must obtain.
Neither of the departments responded to repeated requests for comment clarifying why the ministers granted approval for the mine.

‘Zuma clan’
Oxpeckers reported in May 2015 that Sizwe Zuma had presented himself at public meetings as a director of Atha Africa, and that the mine was being pushed through because of his ties to “the Zuma clan” in northern KwaZulu-Natal.
In the paperwork filed to form the associated BEE company, Sizwe Zuma was listed as a trustee and his residence was given as Bryntirion Estate, the presidential compound in Pretoria. The phone number listed to him on the same paperwork did not work.
Several trustees of one of Atha Africa’s BEE partners, Bashubile Trust, are believed to be relatives of the president, a claim Atha Africa denies.
In a last-ditch effort to halt the mine, the CER plans to take the ministers’ decision to override the Protected Areas Act to court.
“There is no internal appeal to the ministers’ decision, therefore any aggrieved party may approach a relevant court to review the permission in terms of the Promotion of Administrative Justice Act,” the approval letter states.
The company cannot begin work until several legal challenges and roadblocks are cleared.
Mauritz de Bruin of the Endangered Wildlife Trust, who has spent more than a year in Wakkerstroom to oppose proposed mining in various nearby protected environments, said community members have been monitoring the Mabola mine site to ensure work does not begin before legally allowed.
According to De Bruin, there have been several occasions where community members have had to intervene to keep equipment and workers off the site.
“As long as there’s still a battle to be fought, we will fight it,” De Bruin said, though he acknowledged that those opposing the mine are rapidly running out of options.
Atha Africa needs the area to be rezoned by the Dr Pixley Ka Isaka Seme local municipality, although the company’s statement said it “does not foresee any hurdles as the company has all the relevant mining and environmental approvals”.
The CER and its coalition have challenged both the provincial environmental authorisation and the water use licence, which effectively suspends the licence until it is reviewed.
On January 9, Praveer Tripathi, Atha Africa’s senior vice-president, sent an appeal to the department of water and sanitation asking for the suspension of its water use licence to be immediately lifted.
In his letter, Tripathi attacked the CER’s position as an interested and affected party in other mining disputes in the province and accused the NGO of “deliberately sensationalising and disseminating incorrect and/or ambiguous information”.
Tripathi called on the department to lift the suspension by threatening that further delays would be “putting hundreds of millions of dollars of investments and proposed investments at risk, as well as forego[ing] much needed job and community development projects”.
The area’s economy is based on agriculture and tourism. While some residents are in favour of the mine due to the roughly 500 direct jobs promised by Atha-Africa, De Bruin said the promise of local jobs for mines often does not materialise.
“The community members of Wakkerstroom are devastated,” De Bruin said. “They’re quite confused. They don’t understand why [the mine] is possible at all.”
Chief executive of WWF South Africa, Morné du Plessis, described the ministers’ go-ahead as “a worrying turn of events that does not bode well for other protected areas. We are increasingly aware of the trend of diminishing transparency in decisions relating to mining activities.” — oxpeckers.org