Reyna Cacique used to drive eight hours to visit her dad at Pelican Bay State Prison. Their relationship was strong, but it had its ups and downs. In 2015, when she was 20, she hadn't seen him for two or three years.
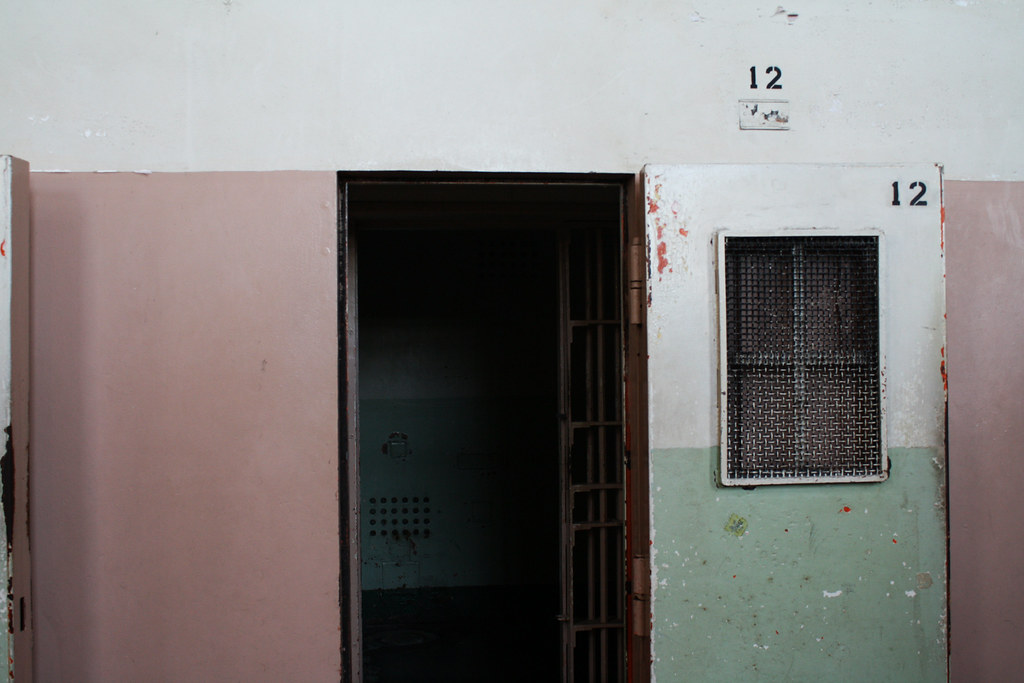
Her father, Rafael Cacique, was in the Secure Housing Unit — being held in a windowless cell the size of a parking space or a handicapped restroom stall — and hadn't seen so much as a blade of grass for more than nine years.
In 2013, Rafael decided he'd had enough. He participated in the largest prisoner hunger strike in U.S. history. About 30,000 prisoners across the state went without food, some for 60 days, to protest California's excessive and inhuman use of solitary confinement.
Public outrage got the wheels in motion for Ashker vs. Governor of California, a class-action lawsuit that ended in a historic settlement in 2015. It resulted in more than 1,600 prisoners being transferred from solitary confinement back to general population prisons.
Most of them had been isolated for more than 10 years.
Cacique was one of the first to be released from the Secure Housing Unit. He was transferred to Corcoran State Prison, where he now has much more incentive to make the most of life on among the general prison population, on the mainline.
I recently spoke with Reyna. She's now 24 and has a 4-year-old-daughter, Lily. What used to be an eight-hour drive to Pelican Bay is now an hour and a half to Corcoran, so she and her daughter go up to visit him practically every month.
"It's been a blessing," Reyna said. "My dad has always taught me the value of family, and when I was pregnant I was like, 'How am I gonna bring my daughter to visit him at Pelican Bay?'"
"Now I know she'll never have to see him the way I did," Reyna said. Starting when she was 10, Reyna's only contact with her father was through a thick sheet of glass. "He and my daughter deserve to have a relationship."
I interviewed both father and daughter, along with a dozen other prisoners around the country, from 2013 to 2015. I visited Rafael at Pelican Bay three times. I wove their stories into a play, a fictionalized account of a hunger strike called "The Box."
Things have improved for Rafa and his family, but will it stay this way?
Before the Ashker settlement, prisoners could only get out of the Secure Housing Unit through snitching, parole or death. Now the California Department of Corrections and Rehabilitation can no longer give prisoners sentences in the SHU with no end. There is a step-down program, a process of rehabilitation, a path back to the mainline in two years or less.
Keep in mind that Juan Méndez, U.N. special rapporteur on torture, said that two weeks of isolation can cause permanent brain damage and therefore should be called "cruel and unusual punishment" or torture.
There is a now a nationwide effort led by 10 states to ban solitary confinement. Colorado now uses the U.N.'s standard of limiting isolation to two weeks, a huge precedent for other states.
The corrections department can no longer sentence prisoners to the Secure Housing Unit based on "gang validation," a designation based on evidence the court ruled unconstitutional, such as having received a birthday card — or artwork with Aztec or Mayan images — from a validated gang member.
For three years, California prisons have been under court observation to ensure these polices are implemented. Early this year, that observation was extended when the judge found "systemic constitutional violations."
Charles Carbone, a lead lawyer on Ashker, goes into California's prisons four times a week. Last month, he spoke with Alberto Talento, a former Mexican mafia member who did 15 years in the Secure Housing Unit based on unconstitutional evidence.
Talento "said he didn't have a future before this happened. I've heard this over and over from guys that got out of the SHU. Guys who've been in gangs since they were 13, 14 years old, now they have an incentive to be upright citizens, to earn respect from their families. They give up the gang life because they have hope the system might work for them … that they might actually have a chance at a better future.
"When you improve prison conditions, humanity expands," Carbone said. "This change in policy has weakened the dominance gangs had in our prisons."
There's also been a shift in how the public sees these men: not as damaged goods we can just throw away, but as human beings who may have made big mistakes and are capable of change.
Meanwhile, the marks of Rafa's extreme isolation haven't left his body or mind, but Reyna likes to see him get some of the respect and care he deserves.